Research
| Research |
| Publications |
| Selected Talks |
| Misc |
| Resume |
| Contacts |
- Three-dimensional model for chemoresponsive polymer gels Presentation
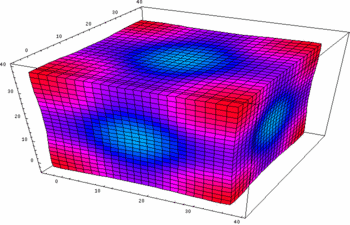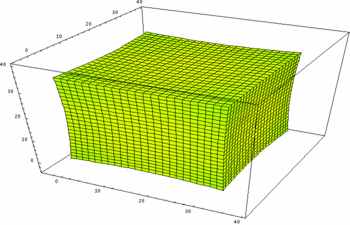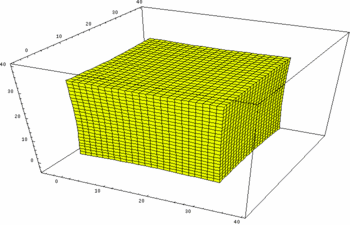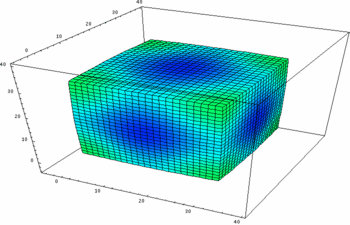
- Modeling Multi-Component Reactive Membranes Presentation
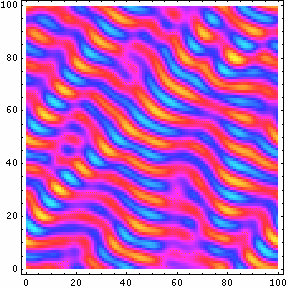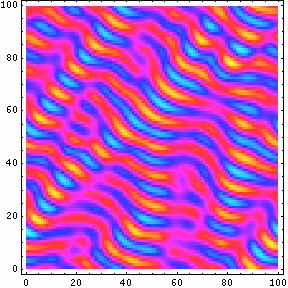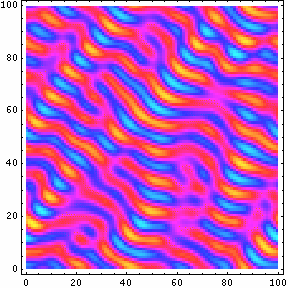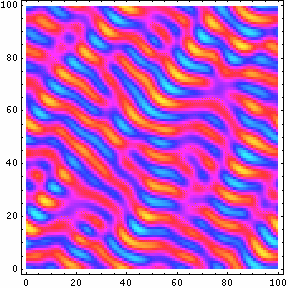
- Dynamics of Ternary Mixtures with Photosensitive Chemical Reactions: Designing Three Dimensional Ordered Composites Presentation
- Modeling chemical reactions in immiscible fluids in microchannels Presentation (windows Only) & PDF file
- Local control of periodic pattern formation in driven binary immiscible fluid Presentation (windows Only) & PDF file
- Binary Fluid within the Microchannels: Morphological instabilities and periodic droplet formation.
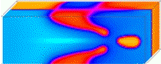
- Binary Fluid within the Microchannels: Mixing and flow control.
- Modeling ternary fluids with reversible chemical reactions.
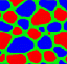
- Lattice-Boltzman modeling.
We used Lattice-Boltzmann modeling for the binary fluids to study:
- The dynamics of the binary fluids within the 2D patterned microchannel:
We have introduced the patterned substrate by means of the appropriate surface potential, decaying away from the substrate.For details, see:
- Olga Kuksenok, J. M. Yeomans, and Anna C. Balazs. Using patterned substrates to promote mixing in microchannels. Phys. Rev. E 65 (3), 031502 (2002).
PDF file - 7,852 KB - Olga Kuksenok, J.M. Yeomans and Anna C. Balazs. Creating localized mixing stations within microfluidic channels. Langmuir 17 (23), 7186-7190 (2001).
PDF file - 1.17 MB
- Olga Kuksenok, J. M. Yeomans, and Anna C. Balazs. Using patterned substrates to promote mixing in microchannels. Phys. Rev. E 65 (3), 031502 (2002).
- Phase separation of a binary fluid with the immobile nanoscale particle. The particles are taken to be wetted by the A (red) fluid.
We found, that:Morphology at late times for: Weak particle/fluid interaction Strong particle/fluid interaction 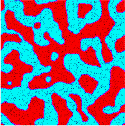

- For sufficiently strong interaction, domains are pinned to finite size at late times
- Hydrodynamics promote the domain grows at early times
- The chemical nature of the particles (effective strength and range of the wetting) essentially alters the dynamics of the phase separation as well as promotes the saturation of the domain size.
- Domenico Suppa, Olga Kuksenok, Anna C. Balazs, and J. M. Yeomans. Phase separation of a binary fluid in the presence of immobile particles: A lattice Boltzmann approach. J. Chem. Phys. 116 (14), 6305-6310 (2002).
PDF file - 695 KB
- The dynamics of the binary fluids within the 2D patterned microchannel:
- Theory of colloidal liquid crystalline systems.
- Theory of dye-doped liquid crystals.
- Theory of radiation effects in organic liquids.